Code tables
Warning
The Niche code tables are published on Zenodo as a reference. These files are used by the package and stored in the niche_vlaanderen/system_tables subdirectory. To check if your current Niche version corresponds to the latest reference data published on Zenodo, check the Zenodo Versions section and compare this with a Niche object output:
>>> from niche_vlaanderen import niche
>>> niche.Niche()
# Niche Vlaanderen version: 1.3
# Using latest niche_vlaanderen 1.3
# Reference values:
# version: 12C <----- Zenodo version used in package
# source: 10.5281/zenodo.10417821
# original file: NICHE_FL_referencegroundwaterlevels_v12C.csv
The steps to create a new release of the package with an updated data set on Zenodo is described in the Package release documentation.
The logic of Niche is largely based on code tables. They convert values (eg mlw, …) to another (eg soil_mlw_class). For categorical data, this happens directly. For continuous data such as nitrogren or mhw, minimum and maximum values are used.
interpretation of minimum and maximum values soil_name
msw_min
msw_max
nitrogen_mineralisation
K1
5000
-5
11
K1
-5
-10
13
K1
-10
-15
15
K1
-15
-20
17
Niche will use the values from the _max column to determine to which category a value has to be added. In this particular case, with a soil_code of 10000 an MSW values ]-5,-10] will give the value 55: the upper limit is included, the lower limit is not. A value of msw=-5 will give nitrogen_mineralisation=50 as a result, a value of msw10 will lead to nitrogen_mineralisation=55. When using real values for mxw, the values will be rounded up to 2 decimals. Eg -50.005 will become -50.01 (< -50) and -50.004 will become -50.00 (=-50).
By default the codetables of the niche_vlaanderen package are used, but the user can supply one or more own codetables (see Niche Configuration file, full example at page bottom; see here for interactive implementation). If real values are used in these codetables, the decimal separator is ‘.’ (note that no real values are used in the existing codetables).
soil_code
The table soil_codes.csv contains the supported soil_codes in NICHE and their corresponding soil_group (used in determining the soil_glg_class, Bepaling bodem_GLG klasse).
management
The table management.csv contains the supported management_codes in NICHE. It also contains a column influence which is used in the calculation of nutrient level.
niche_vlaanderen
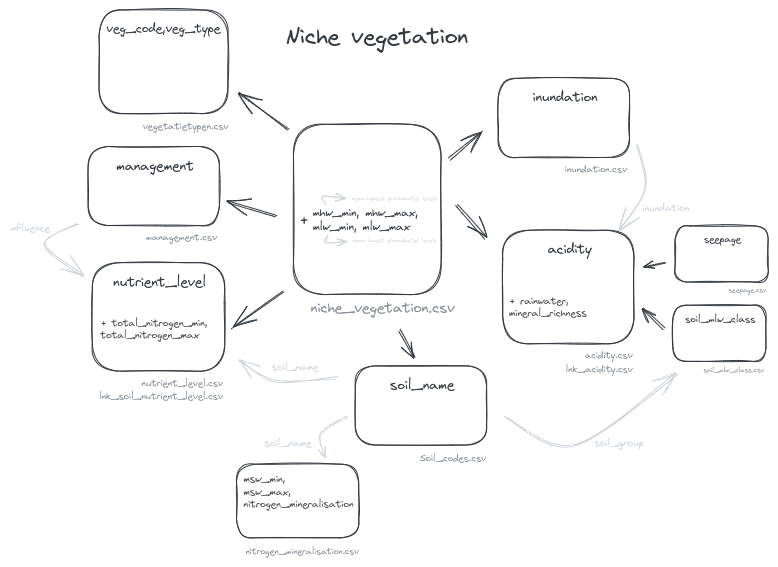
The table niche_vegetation.csv contains the link between the vegetation types that can be predicted by niche and the location factors that govern them.
- Required columns are:
veg_code: vegetation code
veg_type: the vegetation name
soil_code: soil code, must correspond to the Bodemklasse soil_code:.
nutrient_level
acidity
mhw_min, mhw_max:
mlw_min, mlw_max:
management
inundation
Other columns can exist but are ignored.
The lower and upper limits of mhw and mlw are included when classifying.
interpretation of minimum and maximum values veg_code
veg_type
soil_name
nutrient_level
acidity
mhw_min
mhw_max
mlw_min
mlw_max
1
Sphagno-Betuletum
KV
2
1
-20
-1
-38
-20
In the above case, mhw values -20 and -1 both fullfill the required range.
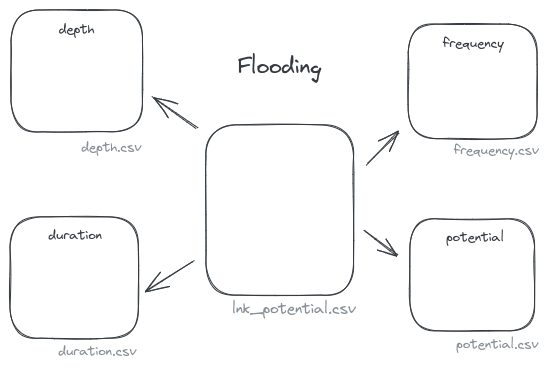
system table relation
The following images illustrate the relation between the individual code tables for respectively niche-vegetation and flooding: